BAMS Social Robot Platform
In one of our previous projects, we developed a mobile robot for hand-eye coordination training to help children with autism retrain their fine motor skills. Our tests and consulting with experts found that interactive social robots have a considerable advantage in interacting with children with ASD (autism spectrum disorder). There are many prominent social robot platforms in the market, but the main problem with utilizing them in ASD rehabilitation is their cost. So, we decided to develop a simple integrated social robot platform for studying the social behaviors of children with ASD and ASD-related rehabilitation. Designing a complex system like social robots is a tedious task that requires multiple generations of prototyping. So, we decided to proceed with this complicated task with an agile development mindset. So, we designed and implemented different parts of the project modular, tested each individually, and then integrated all modules.
 |
|---|
| BAMS 0.0 Facial Expression Module |
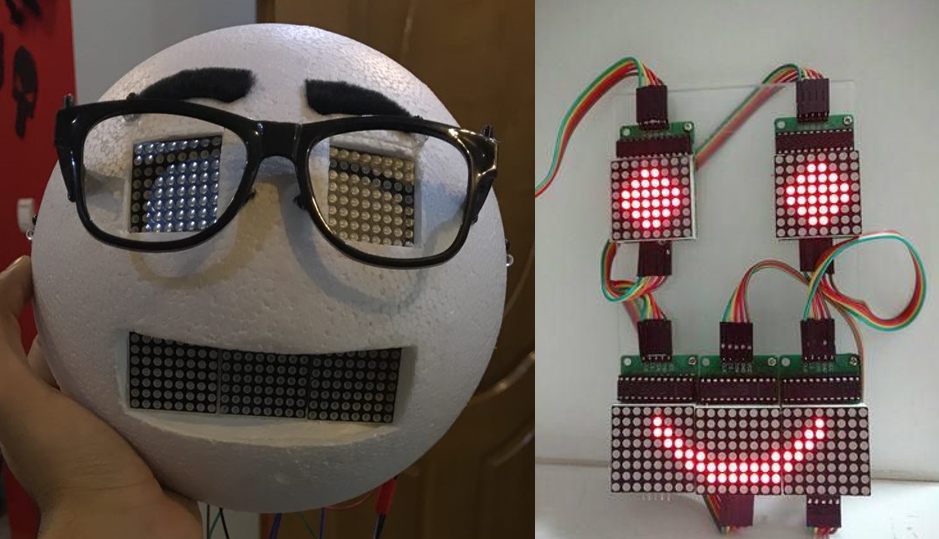
The system design procedure was divided into three subsystems for better task management. The movement module handles robot motion, path planning, collision avoidance, and obstacle detection. The interaction module is responsible for facial expressions, audio feedback, and hand gestures. Lastly, the cognitive module is required for the intelligent behavior of the Robot, including face recognition, voice localization, and emotion recognition. The importance of implementing the software part of the system based on the ROS (Robotic Operating System) ecosystem was self-explanatory from the beginning, so every module was designed and developed based on this to help future integrations. The interaction module was the first step because it could be the system’s most cost-intensive and customizable part. Other than that, ASD experts should confirm its effectiveness in a child-robot interaction scenario. So, we chose to prototype a simple facial expression module and took some feedback from experts. After some consideration, we realized that our initial facial expression unit was far from acceptable, so we had to switch to an LCD-based system.
 |
|---|
| BAMS 1.0 |
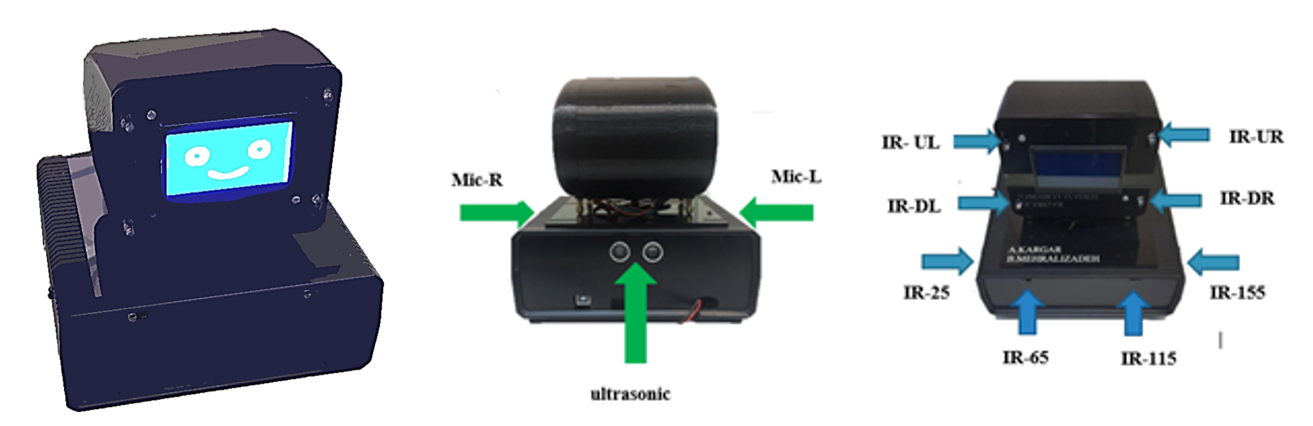
 |
| BAMS 1.0 Interactions |
In this prototype, BAMS 1.0, we prototyped and integrated a few parts for more complicated tests. A cheap character LCD is in the middle of an IR sensor array on a small servo motor that can rotate 180 degrees, and there are two microphones for each Robot’s side. Facial expressions were presented as multiple bitmapped emojis, and the IR sensor array tracked hand movement around the Robot. Also, a basic sound localization system was provided for reaction to the voice commands. All the above functionalities were handled by an Arduino Mega 2560 selected to reduce cost and development time.
 |
|---|
| BAMS 2.0 Movement Module |
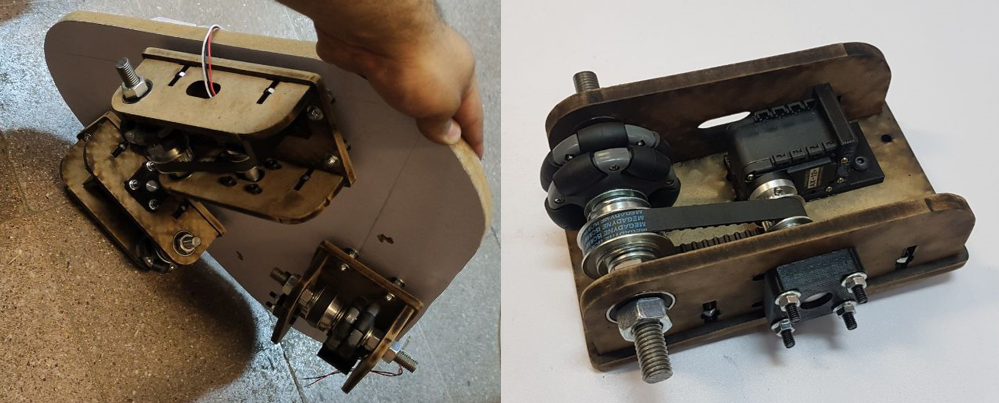
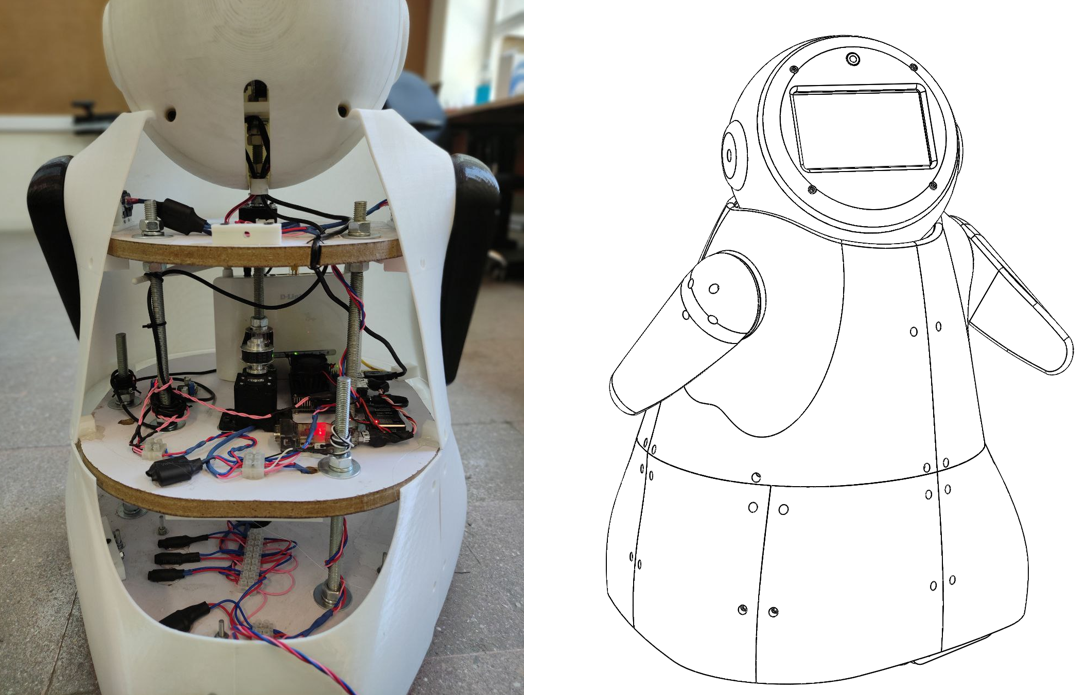
Our previous systems did not have any cognitive module, and their interactions were almost hardcoded on them, but the results and experts’ opinions were promising. Based on what we learned from past experiences, BAMS 2.0 was born, which had all three required modules. The interaction module is based on an Android tablet that presents the Robot’s face. A fisheye lens camera was provided for a wide-angle view. The Robot’s brain is a Nvidia jetson nano that controls all Dynamixel motors with a USB adapter. The Robot is equipped with a local Wi-Fi router for ease of communication. The movement module is based on a triangular Omni wheel vectoring mechanism for the base motion; the Robot’s hands have one degree of freedom each. Other than that, the head of the Robot has 2 degrees of movement provided by a pan-tilt mechanism.
 |
|---|
| BAMS 2.0 |
The BAMS series was a unique experience for my team due to its long and progressive timeline requiring multiple developments and redesign stages. The BAMS 2.0 is now operational in the Advanced Robotics and Intelligent Systems Lab at the University of Tehran, and it will be tested in rehabilitation scenarios for children with ASD. Though the project’s overall cost gradually increased over time, it is still reasonably more affordable than available commercial robots. We hope to open-source all CAD files and source codes soon after publishing our paper.
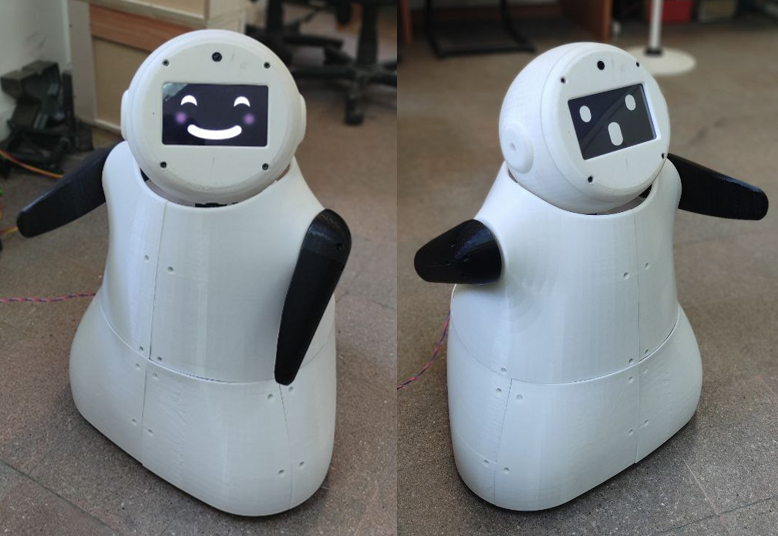 |
|---|
| BAMS 2.0 Interactions |
 |
| BAMS 2.0 Head & Hands Movements |
 |
| BAMS 2.0 Base Motion |