B.bot Mobile Robot
During my M.S. program, I got familiar with ASD (autism spectrum disorder) and the complications it can cause for children’s development. Trouble in social interactions, motor function problems, repetitive movements, and intensive focus on details are some of ASD’s symptoms. Many ASD-related tools have been developed in the Advanced Robotics and Intelligent Systems lab at the University of Tehran, where I attended as a researcher.
The idea of the Mobile Robot and what quirky things we can do with it has always fascinated my team, and we like making toys like devices for children with autism, so we chose hand-eye coordination training as the goal of our little project. The system consists of a robot that can imitate the given path and a minimalistic GUI for human-robot interaction. The Robot is battery-operated, lightweight, and, of course, cost-effective.
Designing such a system always has different challenges; selecting proper hardware, suitable materials, cost, and child-friendly design make the decision-making process problematic. By embracing open-source hardware and software, we significantly decrease the cost and design time, making future developments more straightforward.
This Robot is a two-wheel differential drive robot with two additional contact points inspired by the EPFL Khepera robot chassis. It is built with plexiglass and spacers to make it affordable. The Arduino ecosystem was selected for the circuits and electronics part of projects, particularly its user-friendly interface, to reduce development time. The Arduino Mega 2560 and an L298 motor driver handle the motor control part, and the HC-05 module, connected to Arduino, is responsible for the Bluetooth connection between the human-robot interaction GUI and the Robot.
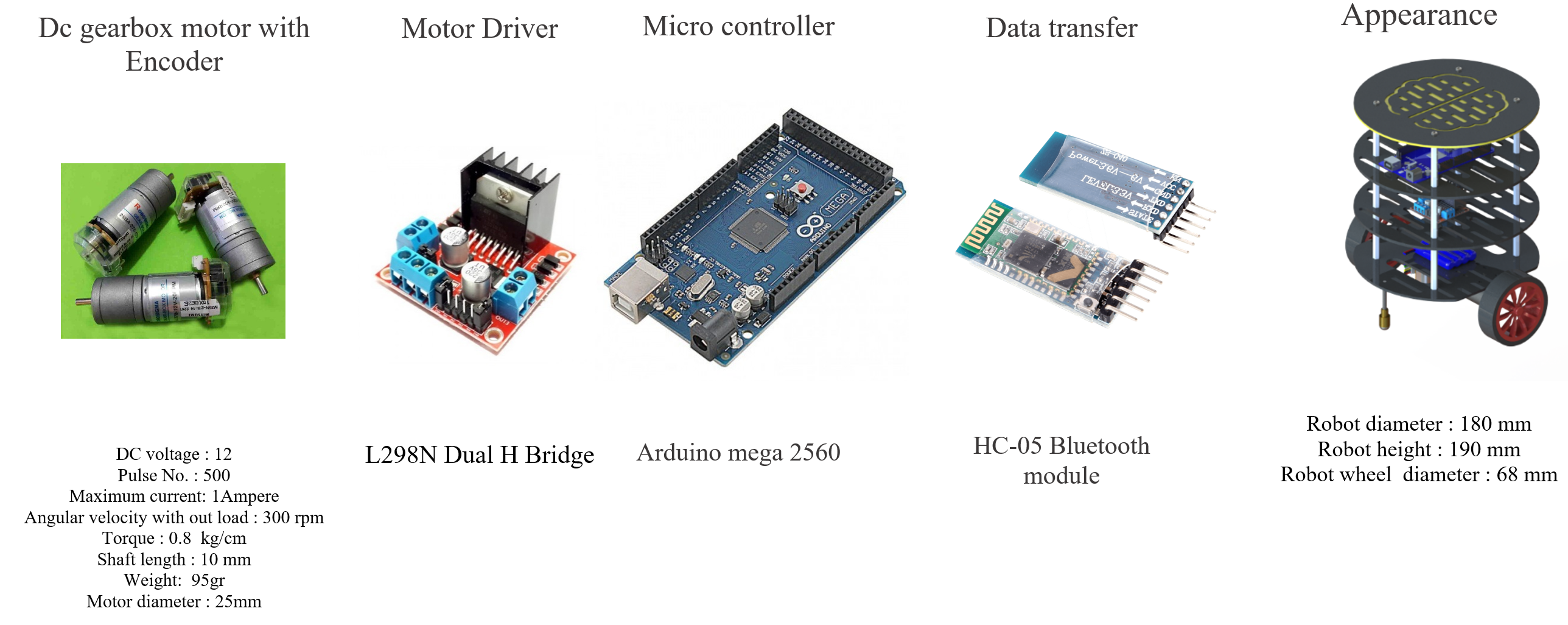 |
|---|
| B.bot configuration |
The software part of the system is divided into two sections: Matlab interface and Arduino motor controller. The Matlab interface provides a simple GUI for drawing a path and a simulation to show the approximate course the Robot will take. It also decomposes the drawn path to multiple checkpoints and sends them over Bluetooth to Arduino, which receives checkpoints and saves them on an array. In the meantime, after receiving multiple checkpoints, the navigation module generates a path based on the given checkpoints and sends it as the motor command.
| Drawn sketch vs. generated path in MATLAB GUI |
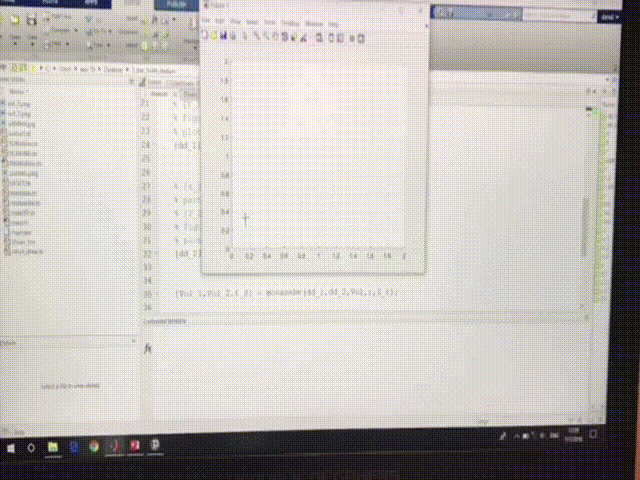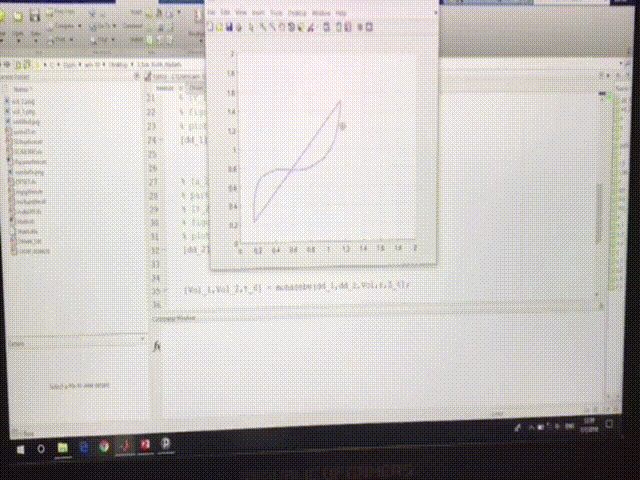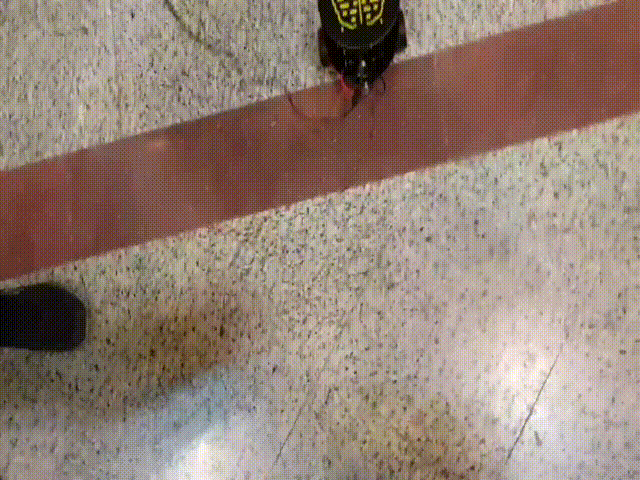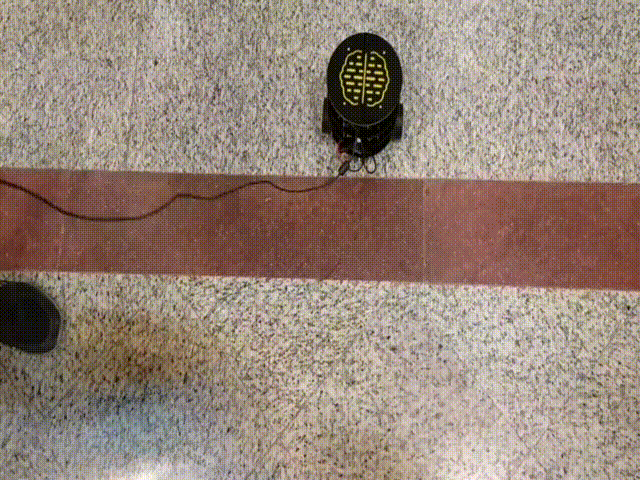 |
| system functioning |